Central venous catheters are highly prevalent in critical care environments and pose a number of serious risks to patients. They require thorough care and assessment by healthcare professionals.
What is a Central Venous Catheter?
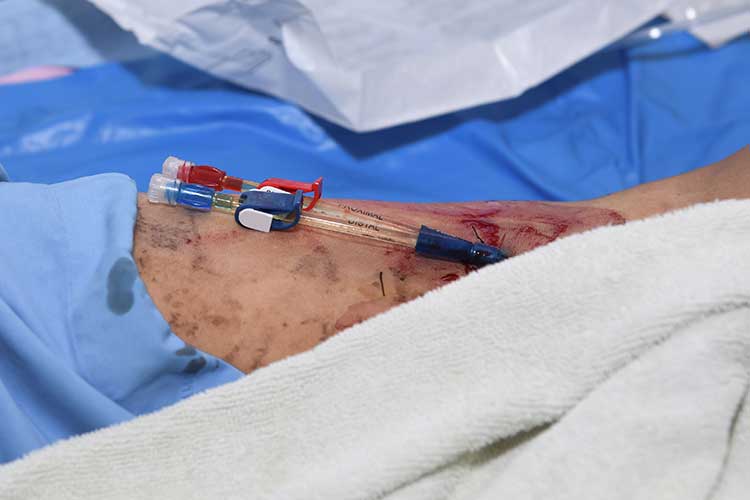
A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line or central venous access device, is a thin, flexible tube used to administer medicines or intravenous fluids and aspirate blood (ATS 2019; Kolikof et al. 2025).
How does a Central Venous Catheter Work?
A CVC is inserted through the patient’s skin and into their body through a peripheral vein or proximal central vein - usually either the internal jugular (neck), femoral vein (groin) or subclavian vein (upper chest). The tip of the CVC should lie on the right side of the heart within either the superior vena cava, the right atrium or the inferior vena cava (Kolikof et al. 2025).
Many CVCs are multi-lumen catheters, meaning they have multiple (generally two to four) internal channels that can deliver several medications to the patient simultaneously (usually dispensing each fluid at a slightly different point along the catheter) (LHSC 2014; Nickson 2024).
Note: Always check whether medications are compatible before ‘piggybacking’ them in the same lumen. Follow your local policies and procedures.
CVC insertion is a standard procedure. However, it does pose a variety of risks (Kolikof et al. 2025).
For this reason, it is important to have a thorough understanding of how to care for a patient with a CVC.
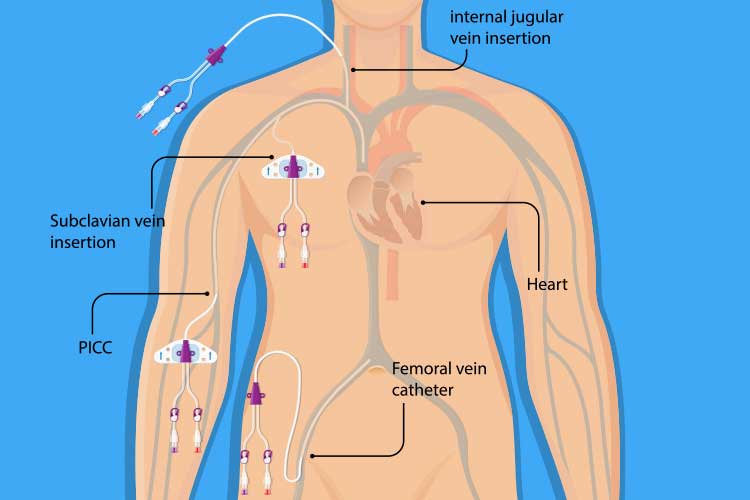
What is a Central Venous Catheter Used for?
In comparison to an intravenous catheter (IV), a CVC is longer, larger and able to stay in situ long-term due to the greater tolerance of large veins. As a result, a CVC provides convenience to not only the clinician but also the patient, as it prevents trauma from repeated needle and catheter insertion (ATS 2019; ACS 2023).
Reasons for using a CVC include, but are not limited to:
- Delivering several medications to a patient simultaneously
- Delivering medication to the patient over a long period of time (e.g. chemotherapy, antibiotics)
- Delivering medication to an outpatient while they are at home (a CVC is less likely to come out of the vein)
- Delivering large amounts of fluid or blood to a patient
- Directly measuring central venous pressure in a large or central vein
- Drawing several blood samples within one day (so that the patient does not need to endure needles every time)
- Delivering nutrition directly into the blood
- Delivering vesicants - drugs that may seriously damage skin and muscle tissue if they leak outside the vein
- Performing dialysis or plasmapheresis
- Enabling insertion of additional devices during complex procedures.
(ATS 2019; ACS 2023; Kolikof et al. 2025)
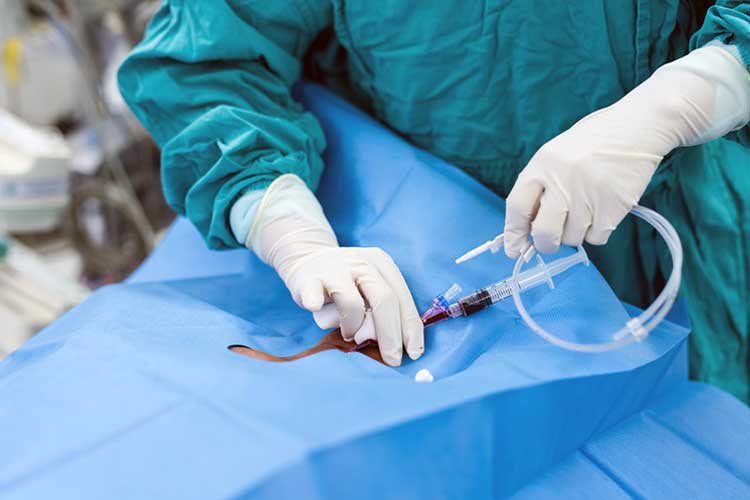
Caring for a Patient with a Central Venous Catheter
When caring for a patient with a CVC in situ, you need to ensure the safety and security of the catheter, have an understanding of which medications are compatible when performing safety checks, and be able to identify any infections of the insertion site. Assessment should be performed at the start of every shift (ACI 2021).
How to perform a CVC assessment:
- Perform hand hygiene; don gloves and personal protective equipment.
- Perform the bed area safety check. CVC assessment is also part of this process.
- Central venous catheters should be transduced prior to their use (critical care setting).
- An appropriate central venous waveform and pressure reading should be seen (critical care setting).
- Perform a head-to-toe assessment.
- Identify the CVC and inspect the insertion site. Look for any signs of infection (e.g. redness, swelling, ooze or pain).
- Establish when the CVC was inserted.
- Ensure an occlusive dressing is intact to reduce risk of infection. If not, you may need to consider changing the dressing (follow hospital protocol when performing a dressing change).
- Transparent semipermeable membrane (TSM) dressings, including those with chlorhexidine, should be replaced every five to seven days.
- Identify how many lumens are present.
- Ensure all intravenous lines are securely connected to the lumens.
- Measure the length of the line from the skin to the first hub - this clarifies how far the line is in the vein and indicates any potential displacement. Refer to hospital protocol if this is the case.
- Traceback each line to the infusion pump to ensure each medicine is connected to the right line.
- Review the patient’s chest X-ray to ensure placement remains correct. If unsure, escalate to the medical team.
- Ensure lines are labelled clearly at the site of the lumens, and the fluid bags containing the medications are also labelled correctly. Identify when each line was last changed and label it accordingly. Follow hospital protocol.
- Ensure multiple medications running on the same lumen are all compatible. Refer to appropriate medication text, as per hospital protocol.
- Ensure luer-lock connections are secure.
- Aspirate and flush any lumen that is free from any lines to ensure patency.
- Report and document any blocked lines that you cannot aspirate blood out of and follow hospital policy.
(ACI 2021; FICM 2023)
Central Venous Catheter Complications
CVC insertion is prone to various complications, including insertion issues, incorrect placement, internal injury and infections (Walsh & Fitzsimons 2023).
Possible complications include, but are not limited to:
- Infections, as catheters inserted into the body make it easier for bacteria from the skin to enter the bloodstream
- Blood clots forming in the vein where the CVC is in situ
- Pneumothorax (collapsed lung) caused by the needle accidentally piercing the lung during insertion (typically during subclavian CVC insertion)
- Air embolism caused by air entering the bloodstream through the catheter. This occurs rarely but is a serious medical emergency
- Side effects caused by incompatible medicines that are being administered together on one lumen
- Catheter fluid leak
- Migration or kinking of the catheter, halting the administration of medication.
(ATS 2019; ACS 2023; ACI 2021; Rabadi et al. 2023)
Conclusion
The risk of complications, some potentially serious, means CVC safety checks are imperative. You must always ensure that medication safety and compatibility are maintained, and the line is secure and safe from harm.
Test Your Knowledge
Question 1 of 3
True or false: Some CVCs can deliver several medications simultaneously.
Topics
Further your knowledge
References
- Agency for Clinical Innovation 2021, Central Venous Access Devices (CVAD), New South Wales Government, viewed 1 May 2025, https://aci.health.nsw.gov.au/networks/icnsw/clinicians/cvad
- American Cancer Society 2023, Intravenous (IV) Lines, Catheters, and Ports Used in Cancer Treatment, American Cancer Society, viewed 1 May 2025, https://www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/planning-managing/tubes-lines-ports-catheters.html
- American Thoracic Society 2019, Central Venous Catheter, American Thoracic Society, viewed 1 May 2025, https://www.thoracic.org/patients/patient-resources/resources/central-venous-catheter.pdf
- The Faculty of Intensive Care Medicine 2023, Invasive Procedure Safety Checklist: CVC Insertion, FICM, viewed 6 May 2025, https://www.ficm.ac.uk/cvc-insertion-safety-checklist-2023
- Kolikof, J, Peterson, K, Williams, C & Baker, AM 2025, ‘Central Venous Catheter Insertion’, StatPearls, viewed 1 May 2025, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557798/
- London Health Sciences Centre 2014, Central Venous Catheters; Central Line CVP; PICC Line, London Health Sciences Centre, viewed 1 May 2025, https://www.lhsc.on.ca/critical-care-trauma-centre/critical-care-trauma-centre-267
- Nickson, C 2024, Central Venous Catheters, Life in the Fast Lane, viewed 6 May 2025, https://litfl.com/central-venous-catheters/
- Rabadi, DK, Abubaker, AK & Almasarweh, SA 2023, ‘Lung Deflation While Placing a Subclavian Vein Catheter: Our Experience in Minimizing the Risk of Pneumothorax’, PLoS One, vol. 18, no. 2, viewed 6 May 2025, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9894405/
- Walsh, EC & Fitzsimons, MG 2023, ‘Preventing Mechanical Complications Associated with Central Venous Catheter Placement’, British Journal of Anaesthesia, vol. 23, no. 6, viewed 6 May 2025, https://www.bjaed.org/article/S2058-5349(23)00035-5/fulltext
 New
New