This article is part of our Training Requirement Series where we provide comprehensive guides to meet the actual training requirements that are often needed/requested of learning and development departments within Australia's healthcare organisations. This series includes both general requirements, such as safety and quality training but also focuses on the specific requirements stemming from the NDIS, Aged Care and NSQHS Quality Standards.
What is Safety and Quality Training?
Safety and quality training in healthcare is a pivotal aspect of ensuring excellence in patient care and safety. Governed by Australian healthcare standards, this training is instrumental in maintaining a high standard of healthcare services.
Safety and Quality Training involves instructing healthcare staff in practices necessary to ensure safety and quality in healthcare delivery. It covers a range of topics, from infection control to patient rights, and aims to align with the standards set by the Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care (ACSQHC).
The Importance of Safety and Quality Training in Healthcare
This training is essential for improving patient outcomes, reducing the risk of harm, and ensuring regulatory compliance. It also helps in building a culture that values patient safety and quality care, which is vital for the reputation and efficiency of healthcare organisations.
What is the "Safety and Quality Training" Training Requirement?
Adherence to the NSQHS Standards (actions 1.19, 1.20, and 1.21), Aged Care Standards (7.3(d)), and the Strengthened Standards (2.9.4-2.9.6) is essential. These standards outline the responsibilities of healthcare organisations in providing regular, comprehensive training to their staff.
Relevant Standards
The roles and responsibilities are outlined by the health organisations for safety and quality for:
- Members of the governing body
- Any employed, contracted, locum, agency, student or volunteer of the organisation
The health organisation uses training systems to:
- Assess training needs and competency of its workforce
- Implement mandatory training programs to meet requirements stemming from the Standards
- Provide access to training in order to meet the safety and quality training needs
- Monitor the workforce's participation in training
The health organisation has strategies to improve the cultural awareness and cultural competency of the workforce to meet the needs of its Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander patients
National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards
Requirement 7.3: Workforce competence, qualification, and training standards:
- c) The workforce is competent and members of the workforce have qualifications and knowledge to effectively perform their roles.
- d) The workforce is recruited, trained, equipped and supported to deliver the outcomes required by the Standards.
Action 2.9.4: Workforce training systems
The provider maintains and implements a training system that:
- a. includes training strategies to ensure that workers have the necessary skills, qualifications and competencies to effectively perform their role
- b. draws on the experience of older people to inform training strategies
- c. is responsive to feedback, complaints, incidents, identified risks and the outcomes of regular worker performance reviews.
Action 2.9.5: Reviewing and improving workforce training systems
The provider regularly reviews and improves the effectiveness of the training system.
Action 2.9.6: Competency-based training
All workers regularly receive competency-based training in relation to core matters, at a minimum:
- a. the delivery of person-centred, rights-based care
- b. culturally safe, trauma aware and healing informed care
- c. caring for people living with dementia
- d. responding to medical emergencies
- e. the requirements of the Code of Conduct, the Serious Incident Response Scheme, the Quality Standards and other requirements relevant to the worker’s role.
Action 2.9.7: Worker assessments, monitoring, and reviewing
The provider undertakes regular assessment, monitoring and review of the performance of workers.
Strengthened Quality Standards framework analysis - Aged Care Quality Standards
Failure to comply with the requirements could lead to an organisation being penalised or reprimanded.
Skills Required for Safety and Quality Training
A range of skills are essential for effective implementation of safety and quality training. The following table outlines the key skills necessary for healthcare professionals to ensure the delivery of safe and high-quality care.
- Knowledge of Healthcare Standards: Understanding and application of relevant healthcare standards and regulations.
- Risk Assessment and Management: Skills to identify, evaluate, and mitigate risks in healthcare settings.
- Effective Communication: Ability to communicate clearly and empathetically with patients, families, and colleagues.
- Patient-Centred Care: Skills to provide care that respects and responds to individual patient preferences and needs.
How to Assess Staff Competency in Safety and Quality Training
Assessing the competency of healthcare staff in safety and quality practices is a multi-faceted process. The following methods are employed to ensure that staff are not only knowledgeable but also proficient in applying these principles in their day-to-day operations.
- Direct Observation: Supervisors observe staff in their daily duties to evaluate their application of safety and quality standards.
- Simulations: Realistic scenarios are used to assess how staff respond to emergencies or challenging situations.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Includes peer reviews and patient feedback to gauge the effectiveness of staff interactions and care delivery.
- Theoretical Evaluations: Written or online tests to assess understanding of safety and quality principles.
- Self-Assessment: Staff are encouraged to reflect on their practices and identify areas for improvement.
Strategies to Support Healthcare Staff Develop Skills in Safety and Quality Training
Supporting the development of employee skills in safety and quality is a continuous process. The following strategies can be employed by healthcare organisations to enhance their staff's competencies in these critical areas.
- Implementing regular training workshops on different aspects of safety and quality.
- Providing hands-on experience through simulated training exercises.
- Establishing mentorship programs for knowledge and skill transfer.
- Encouraging peer review programs to foster a culture of continuous learning and feedback.
- Offering online courses and resources for self-paced learning.
Sample Training Plan for the Safety and Quality Training Requirement
A structured training plan is essential for developing quality improvement skills.
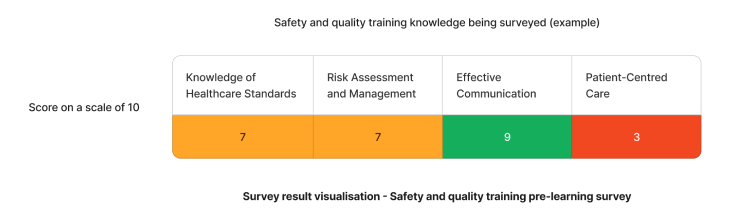
Using the above needs assessment survey as an example - The skill requiring the most attention for safety and quality training are person-centred care. We can target learning initiatives to fill these gaps to enhance staff competency.
| Quarter | Topics | Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Person-centred care |
Need an LMS that can support safety and quality training?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support with your training requirement needs!
Staff Competency Assessment for Safety and Quality Training - Example
Assessing the skills of healthcare staff in safety and quality training can be effectively done through targeted survey questions. The following questions are designed to evaluate staff knowledge and application of safety and quality principles in healthcare.
Staff Survey - Safety and Quality Training Competency
-
How do you ensure compliance with safety protocols in your daily tasks?
- [Answer here]
-
Describe a situation where you had to use your communication skills to resolve a patient issue.
- [Answer here]
-
What are your strategies for staying informed about the latest healthcare safety and quality standards?
- [Answer here]
-
How would you manage a situation where safety standards are compromised?
- [Answer here]
-
Can you provide an example of how you have contributed to a culture of safety and quality in your workplace?
- [Answer here]
Conclusion
Safety and quality training in healthcare is vital for ensuring patient safety and delivering high-quality care. This comprehensive guide provides Learning and Development Coordinators with the necessary information to develop and implement effective training programs. By focusing on skill development, competency assessment, and continuous improvement, healthcare organisations can meet and exceed the standards set by Australian healthcare regulatory bodies.
References
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'Clinical Governance Standard'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 1.19'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 1.20'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 1.21'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Requirement 7.3 (c-d)'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Stronger Standards, Better Aged Care Program - Action 2.9.4-2.9.7'


