This article is part of our Training Requirement Series where we provide comprehensive guides to meet the actual training requirements that are often needed/requested of learning and development departments within Australia's healthcare organisations. This series includes both general requirements, such as high-risk medicines, but also focuses on the specific requirements stemming from the NDIS, Aged Care and NSQHS Quality Standards.
What is a 'Medicines List'?
A medicines list is a detailed document that provides comprehensive information about the medicines a patient is currently taking or has been prescribed. This includes over-the-counter medicines, prescribed medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. The list aims to improve communication among healthcare providers and between patients and providers, reducing the risk of medication errors.
Examples of Medicines List Provision in Healthcare
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) Integrations: Seamless integration with EHR systems allows for automatic updates to a patient's medication list, ensuring accuracy and accessibility across different healthcare providers.
- Patient-Held Medicine Lists: Encouraging patients to maintain their own up-to-date medicines lists, which they can share with each healthcare provider they visit.
- Pharmacist Review: Pharmacists review and confirm the accuracy of patients' medicines lists, providing an extra layer of verification to reduce errors.
- Clinical Health Information Systems: These platforms facilitate the secure exchange of healthcare information, including medicines lists, between different healthcare systems and providers.
What is the “Medicines List Provision” Requirement?
Under NSQHS Standard 4, Action 4.12, healthcare organisations are required to ensure that a current medicines list is available to patients and all their healthcare providers, both within and outside the organisation. This requirement is crucial for coordinating care and safely managing medicines across different care settings.
Relevant Standards
Action 4.12: Provision of a medicines list
The health service organisation has processes to:
Clinicians review a patient’s current medication orders against their best possible medication history and the documented treatment plan, and reconcile any discrepancies on presentation and at transitions of care
Action 4.06: Medication reconciliation
The health service organisation has processes to:
- (a) Generate a current medicines list and the reasons for any changes
- (b) Distribute the current medicines list to receiving clinicians at transitions of care
- (c) Provide patients on discharge with a current medicines list and the reasons for any changes
National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards
Action 5.3.5: High-Risk Medications Management:
- Providers must implement processes to identify, monitor, and mitigate risks to older people associated with high-risk medication usage. This includes reducing inappropriate use of psychotropic medicines
Strengthened Quality Standards framework analysis - Aged Care Quality Standards
Failure to comply with the requirements could lead to an organisation being penalised or reprimanded.
Related Training Requirements Guides
The following Training Requirement guides can be used to support and facilitate the "Provision of a medicines list" training requirement:
What Skills Do Staff Need For The Medicines L:ist Provision Requirement?
Staff need to develop specific skills to effectively manage and provide an accurate medicines list. These include:
| Skill | Key Elements |
|---|---|
| Medication Reconciliation Skills |
Critical for ensuring the consistency and accuracy of medicine lists across different healthcare settings, helping to avoid potentially harmful discrepancies. |
| Attention to Detail |
Essential for accurately recording and reviewing medication names, dosages, and schedules, reducing the risk of errors in medication administration. |
| Communication Skills |
Vital for the effective exchange of medication-related information among healthcare professionals and between healthcare professionals and patients, ensuring clarity and understanding. |
| Documentation and Compliance |
Expertise in maintaining meticulous records for legal and clinical safety reasons, while strictly adhering to privacy regulations and other guidelines set by bodies like the Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care. |
| Technical Skills |
Necessary for proficiently using electronic health records (EHRs) and other digital tools to update, maintain, and access comprehensive medication information efficiently. |
How to Assess Staff Competency in Medicines List Provision Requirement?
Assessing staff competency involves both direct observation and evaluation of knowledge through assessment or simulations. Feedback from colleagues and patients can also provide insight into a staff member's competency in managing medicines lists.
- Regular training sessions: Providing employees with frequent educational sessions to enhance their understanding of how to manage and reconcile various medication lists effectively, ensuring accuracy and safety in patient care.
- Effective communication and documentation practices: Organising workshops focused on improving how employees communicate with colleagues and patients, as well as how they document medication information, to minimise errors and improve healthcare outcomes.
- Peer Reviews: A 360-degree feedback mechanism involving colleagues, superiors, and sometimes patients can provide a holistic view of one's competency.
- Evaluation: Regular, structured assessments through performance appraisals and competency checklists to ensure ongoing proficiency in handling Medicines list .
Strategies to Support Employees Enhance Skills in Medicines List Provision
Creating a culture of learning on provision of a medicines list safety is vital. Once staff competency levels are identified, targeted training interventions can be formulated.
Here are some strategies:
- Educational Workshops: Workshops focus on enhancing the ability of healthcare workers to communicate effectively with both colleagues and patients and to maintain precise documentation, which is essential for accurate medication management.
- Technology-based learning tool :Leveraging the latest technology tools and platforms for educational purposes helps keep healthcare professionals abreast of current trends and practices.
- Communication and documentation practices:: The ability of healthcare workers to communicate effectively with both colleagues and patients and to maintain precise documentation, which is essential for accurate medication management.
Sample Skills Development Training Plan for Provision of a Medicines list Requirement
Staff need to develop specific skills to effectively manage and provide an accurate medicines list. These include:.
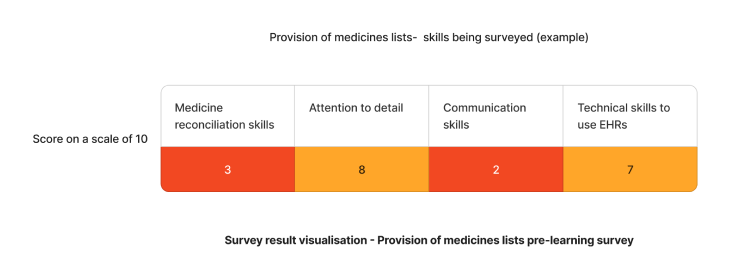
- Medication reconciliation skills: Ensures accuracy between various medication lists.
- Attention to detail: Accurately record medication names, dosages, and schedules.
- Communication skills: to effectively share information with other healthcare professionals and patients.
- Technical skills to use EHRs: and other digital tools for updating and accessing medication information.
Need training for provision of a medicines list in your organisation?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support with your provision of a medicines list!
How to Assess Staff Competency in the Provision Medicines List- Example
Assessing staff competency involves both direct observation and evaluation of knowledge through quizzes or simulations. Feedback from colleagues and patients can also provide insight into a staff member's competency in managing medicines lists.
Sample Skills Staff Survey - Provision of Medicines List
-
Do you feel confident in your ability to accurately compile a medicines list for patients?
- 1. Yes
- 2. Somewhat
- 3. No
-
How comfortable are you with using electronic health records (EHRs) to update and access medicines lists?
- 1. Very comfortable
- 2. Somewhat comfortable
- 3. Not comfortable at all
-
Do you understand how to identify and rectify discrepancies in medicines lists across different care settings?
- 1. Yes, completely
- 2. I have some understanding
- 3. No, I need more training
-
Can you effectively communicate medicines list information to other healthcare professionals and patients?
- 1. Yes, confidently
- 2. Somewhat confidently
- 3. No, I struggle with this
-
How often do you verify the accuracy of medicines lists with patients or their carers?
- 1. Always
- 2. Sometimes
- 3. Rarely
-
Do you feel you have received adequate training on the importance of and how to maintain an up-to-date medicines list?
- 1. Yes, definitely
- 2. Partially
- 3. No, I need more training
Conclusion
The successful implementation of a training program for the provision of a medicines list requires a multifaceted approach. It involves not only understanding the fundamental aspects of what a medicines list is and the specific requirements set forth by healthcare standards but also focuses heavily on developing, assessing, and continuously improving the relevant skills of healthcare staff. By embracing a comprehensive training strategy that includes regular educational sessions, practical workshops, feedback mechanisms, and structured evaluations, healthcare organisations can significantly enhance the competency of their staff in providing accurate and up-to-date medicines lists.
References
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2024. NSQH Action 4.12-'Provision of a medicines list'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2024. NSQHS Action 4.06 - 'Medication reconciliation'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2024. Strengthened Standards 5.3.5- 'High-Risk Medications Management
- Beuscart, JB, Pelayo, S, Robert, L, Thevelin, S, Marien, S & Dalleur, O, 2021, 'Medication review and reconciliation in older adults', European geriatric medicine, vol. 12, pp.499-507.
- Chaghari, M, Saffari, M, Ebadi, A & Ameryoun, A, 2017, 'Empowering education: A new model for in-service training of nursing staff', Journal of Advances in Medical Education & Professionalism, vol.5, no.1, p.26.
- Mardani, A, Griffiths, P & Vaismoradi, M, 2020, 'The role of the nurse in the management of medicines during transitional care: a systematic review', Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare, vol. 13, pp.1347-1361.


