This article is part of our Training Requirement Series where we provide comprehensive guides to meet the actual training requirements that are often needed/requested of learning and development departments within Australia's healthcare organisations. This series includes both general requirements, such as prescribing and administering blood and blood products but also focuses on the specific requirements stemming from the NDIS, Aged Care and NSQHS Quality Standards.
What is Blood Prescription and Administration?
Developing a training program for healthcare organisations, in alignment with the National Safety and Quality Health Service Standards (NSQHS) - specifically Action 7.06, is critical for enhancing patient care and safety. This article outlines the essential components of such a program, focusing on the prescription and administration of blood and blood products. Procedures are implemented to guarantee the proper clinical utilisation of blood and blood products, with approaches adopted to lower the associated transfusion risks.
Why is Prescribing and Administering Blood and Blood Products Important?
These procedures play a crucial role in the medical field, significantly impacting patient care and treatment outcomes. They are particularly essential in scenarios where patients are grappling with life-threatening conditions or undergoing critical medical interventions.
Below are some detailed explanations and examples of how these procedures make a difference, please note that there many other safety checks that must be adhered to, the list below serves as a general outline:
- Severe Anemia: Blood transfusions are a cornerstone treatment, replenishing the body's red blood cell count to transport oxygen effectively.
- Clotting Disorders: Providing patients with the necessary blood products can help manage conditions like hemophilia, preventing excessive bleeding.
- During Surgeries: Blood loss during operations can be significant. Administering blood products ensures that patients maintain stable vital signs and recover more efficiently.
- Right Product: Ensures compatibility and meets the specific needs of the patient’s condition, whether that be red cells, platelets, plasma, or others.
- Right Patient: Utilises precise identification and cross-matching processes to prevent adverse reactions and ensure patient safety.
- Right Time: Timely administration is critical, especially in emergencies, to prevent complications or deterioration of the patient's condition.
By focusing on these aspects, healthcare professionals can significantly reduce the risks associated with transfusions, such as allergic reactions, infections, and complications related to incorrect blood type compatibility, thereby enhancing overall patient outcomes. These strategies and careful attention to detail are fundamental in promoting safety and efficacy in the use of blood and blood products in medical treatments.
What is the “Blood and Blood Product Prescription and Administration” Training Requirement?
Under NSQHS Standard 7 - Blood Management, Action 7.06 mandates healthcare organisations to ensure staff are competent in prescribing and administering blood products, including adherence to guidelines, monitoring, and managing adverse reactions.
Relevant Standards
The health service organisation supports clinicians to prescribe and administer blood and blood products appropriately, in accordance with national guidelines and national criteria
National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards
Failure to comply with the requirements could lead to an organisation being penalised or reprimanded.
Related Training Requirements Guides
The following Training Requirement guides can be used to support and facilitate the blood management events training requirement:
What Skills Do Staff Need For Prescribing and Administering Blood and Blood Products?
Staff involved in these procedures must possess a range of skills:
- Knowledge of blood product types and indications: This involves understanding the different types of blood products (such as red blood cells, platelets, and plasma) and their specific clinical uses. It requires familiarity with indications for transfusion, ensuring the correct product is chosen for each patient's condition.
- Understanding of transfusion risks and consent processes: Recognising potential transfusion-related risks, such as allergic reactions, infections, and transfusion reactions, and ensuring patients are informed about these risks as part of the consent process. This understanding is crucial for ethical and legal compliance.
- Competence in administering products: Safely administering blood products involves following strict protocols to prevent errors, monitoring patients for any signs of adverse reactions during and after the transfusion, and taking appropriate actions if necessary.
- Able to identify patient deterioration: Entails the prompt recognition of early signs that a patient's condition is worsening, particularly after transfusions, to ensure immediate and appropriate interventions are taken
- Skill in managing adverse reactions: The ability to quickly identify signs of adverse reactions to transfusions, such as fever, allergic responses, or more severe conditions like transfusion-related acute lung injury, and to initiate appropriate treatment and management strategies promptly.
- Accurate Documentation: Involves meticulously recording all relevant information related to the prescription and administration of blood products. This includes details of the blood product type, dosage, administration time, and any observations or patient reactions. Accurate documentation is crucial for ensuring continuity of care, legal compliance, and facilitating quality improvement and patient safety initiatives.
How to Assess Staff Competency in Prescribing and Administering Blood and Blood Products?
Assessing competency involves both theoretical knowledge and practical skills evaluation, through written tests, direct observation, and simulation exercises. It's crucial to establish clear criteria and use a structured assessment tool.
- Written Tests: Evaluate theoretical knowledge and understanding of guidelines, types of blood products, and their indications. Tests can cover safety protocols, dosing calculations, and recognition of transfusion-related risks.
- Direct Observation: Supervisors or trained assessors observe staff during the actual administration of blood products, assessing adherence to protocols, safety practices, and the ability to respond to patient needs and potential adverse reactions.
- Simulation Exercises: Staff participate in controlled simulation scenarios that mimic real-life situations, allowing evaluators to assess practical skills in a safe environment. This includes the handling of emergencies, such as managing transfusion reactions.
- Structured Assessment Tools: Use of detailed checklists or rating scales to systematically evaluate and document competencies in both theoretical knowledge and practical skills, ensuring a comprehensive assessment of each staff member's abilities.
- Feedback and Continuous Learning: Providing detailed feedback following assessments to support ongoing learning and improvement. Encouraging engagement with further education and training opportunities to enhance skills and knowledge.
Strategies to Support Employees Enhance Skills in Prescribing and Administering Blood and Blood Products
Enhancing skills can be achieved through:
- Regular in-service training sessions
- Simulation-based learning for hands-on practice
- Access to online resources and up-to-date guidelines
- Peer review sessions for case discussions
- Mentorship programs for ongoing support and guidance
Sample Training Plan for the Prescribing and Administering Blood and Blood Products
A detailed training plan is critical for skill development in Prescribing and Administering Blood and Blood Products. Below is an extended sample plan:
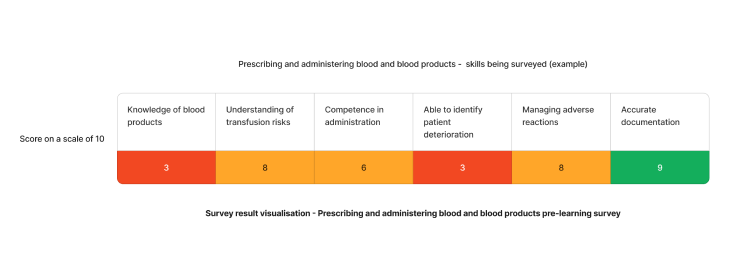
Using the above needs assessment survey as an example - The skill requiring the most attention for Prescribing and administering blood and blood products in healthcare are ability to identify signs of patient deterioration and knowledge of blood products. We can target learning initiatives to fill these gaps to enhance staff competency.
| Quarter | Topics | Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Ability to identify signs of patient deterioration |
|
| Q2 | Knowledge of blood products |
Need an LMS that can support prescribing and administering blood and blood products?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support with your training requirement needs!
Staff Competency Assessment for Prescribing and Administering Blood and Blood Products- Example
Consider the following survey questions to evaluate staffs recognising and reporting adverse events:
Staff Survey - Assess Reporting Adverse Blood Management Events Competency
-
How confident do you feel in identifying and managing adverse reactions related to blood transfusions?
- [Answer here]
-
How familiar are you with the organisation's procedures for prescribing and administering blood and blood products?
- [Answer here]
-
Have you encountered any challenges in prescribing and administering blood products? If so, please describe?
- [Answer here]
-
In your opinion, what areas of training could be improved to enhance your skills in prescribing and administering blood and blood products?
- [Answer here]
-
In what ways could the process of prescribing and administering be improved to ensure safer and more effective management of blood and blood products?
- [Answer here]
Conclusion
In conclusion, the competency of healthcare staff in prescribing and administering blood and blood products is paramount for patient safety and the effective management of blood transfusions. By employing a comprehensive assessment approach that includes surveys, direct observation, and continuous training, healthcare organisations can ensure their staff are equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills. This not only enhances patient care but also minimises the risks associated with blood transfusion, ultimately leading to better health outcomes for patients. It is essential for healthcare organisations to continually support and develop their staff's capabilities in this critical area of medical practice.
References
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'Blood Management Standard'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 7.06'
- Australian Red Cross, 2024. Adverse Events
- Leahy, MF, Hofmann, A, Towler, S, Trentino, KM, Burrows, SA, Swain, SG, Hamdorf, J, Gallagher, T, Koay, A, Geelhoed, GC & Farmer, SL, 2017, 'Improved outcomes and reduced costs associated with a health‐system–wide patient blood management program: a retrospective observational study in four major adult tertiary‐care hospitals', Transfusion, vol.57, no.6, pp.1347-1358.
- Kable, A, Kelly, B & Adams, J, 2018, 'Effects of adverse events in health care on acute care nurses in an Australian context: A qualitative study', Nursing & Health Sciences, 20(2), pp.238-246.
- World Health Organization, 2019. Blood Transfusion Safety


