This article is part of our Training Requirement Series where we provide comprehensive guides to meet the actual training requirements that are often needed/requested of learning and development departments within Australia's healthcare organisations. This series includes both general requirements, such as patient or client deterioration, but also focuses on the specific requirements stemming from the NDIS, Aged Care and NSQHS Quality Standards.
What is Patient Deterioation?
Deterioration implies a sudden decline in a patient’s condition. It could manifest physically, mentally, or functionally, necessitating quick intervention (Stelfox, Bagshaw, & Gao, 2015).
Addressing patient deterioration is paramount in healthcare. This article outlines a training guide based on national standards.
What is the 'Patient Deterioration' Training Requirement?
Training is mandated under NSQHS, Aged Care Quality Standards, and Strengthened Aged Care Quality Standards to ensure negative patient and client outcomes are minimised.
Below are the standards that are related to identifying and responding to patient or client deterioration.
Relevant Standards
Action 8.04: Patient monitoring processes
- Patients have vital sign monitoring plans, which are individualised and monitored as required based on the plan
- Changes in observations are documented to detect acute deterioration over time
Action 8.05: Recognising acute deterioration in patient mental state
- Use comprehensive care plans to guide monitoring patients susceptible to mental state deterioration
- Workforce members are made aware and alert to these patients
- Workforce members are made aware and alert to signs of delirium
- Workforce can instigate initial response to keep patients safe until specialist review arrangements are made
Action 8.10: Deterioration response systems
- Processes are in place to ensure clinicians with appropriate skills manage acute deterioration episodes
Action 8.11: Deterioration support
- Processes are in place to ensure at least one clinician (with relevant skills) is available at all times for rapid access, and can deliver advanced life support
Action 8.12: Mental state escalation processes
- Escalation processes are in place for patient's experiencing deterioration - including designation of responsibilities and roles for staff (including timeframes for response)
- Partnerships with relevant organisations are in place if responding to acute mental state deterioration is outside of your organisation's services
- Staff are aware of and use (where necessary) the escalation protocol
Action 8.13: Physical deterioration management and referrals
- Causes of acute deterioration are mapped against your organisation's capacity to ensure definitive management
- Systems are in place for rapid referral to other services if your organisation cannot provide definitive care
National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards
- Client deterioration (mental health, cognitive or physical function) of capacity or condition is recognised and responded to in a timely manner
Action 3.2.5 (b): Identifying deterioration
- Client deterioration is identified (or changes to their ability to perform daily activities, mental state, cognitive or physical function, capacity or condition)
Strengthened Quality Standards framework analysis - Aged Care Quality Standards
Related Training Requirement
The following Training Requirement guides can be used to support and facilitate the 'patient/client Deterioration Training Requirement'
Failure to comply with the requirements could lead to an organisation being penalised or reprimanded.
How to Identify Patient or Client Deterioration
Early identification of patient deterioration is crucial to ensure the patient receives timely care to further minimise negative health outcomes. A head to toe assessment must be performed on the patient including vital signs.
Vital signs include:
- Blood Pressure
- Temperature
- Oxygen saturation
- Respiratory rate
- Heart Rate
Head to Toe assessment includes the following body systems:
- Neurological
- Cardiovascular
- Respiratory
- Gastrointestinal
- Renal
- Musculoskeletal
- Integumentary
- Social
The Early Warning Score (EWS) consolidates these factors into a single score, triggering action when a threshold is crossed (Gerry, et al. 2020).
How to Respond to Patient/Client Deterioration
Once deterioration is identified, immediate action is required. The following steps are crucial:
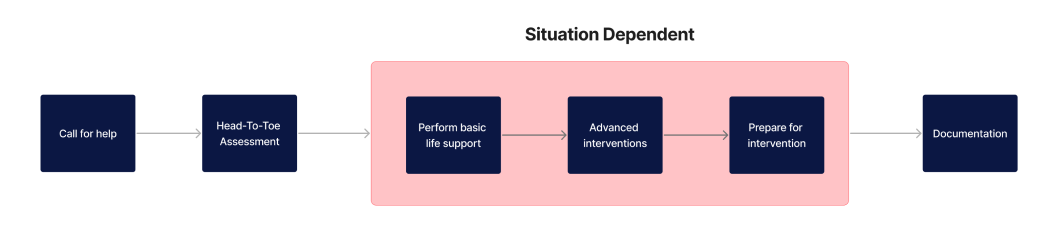
- Call for help: Immediately summon additional healthcare staff or emergency services. The gravity of the situation requires prompt collective action.
- Perform a head-to-toe assessment including patient history: Conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's condition, checking vital signs and inquiring about medical history, to inform the subsequent course of action.
- Perform basic life Support if required: If the patient is unconscious or unresponsive, initiate basic life support measures such as CPR, while waiting for advanced medical intervention.
- Follow escalation protocol within your organisation: Adhere to your healthcare facility’s established guidelines for escalating the care of a deteriorating patient. This may involve alerting specific medical teams or transferring the patient to a higher level of care.
- Prepare for intervention: Assemble necessary equipment and medications in anticipation of medical interventions, ensuring everything is at hand for quick access.
- Documentation: Meticulously document all actions taken, assessments performed, and the patient's response to interventions. Accurate record-keeping is crucial for both ongoing care and quality assurance.
Skills Required by Healthcare Staff for Identifying and Responding to Patient/Client Deterioration
Identifying and responding to patient deterioration are complex tasks that require a multi-faceted skill set. Here, we break down these essential skills:
| Skill | Key Elements |
|---|---|
| Observation Skills |
|
| Communication Skills |
|
| Clinical Judgement |
|
| Technical Skills (Staff require appropriate training for this area) |
|
| Soft Skills |
|
How to Assess Staff Competency in Identifying and Responding to Patient or Client Deterioration
Effective assessment of staff competency ensures that healthcare professionals are adequately prepared for clinical and situational scenarios involving patient or client deterioration. The following methods are commonly employed:
- Objective Structured Clinical Examinations (OSCE): Provides a controlled environment to evaluate clinical skills. Staff are observed performing specific tasks or managing simulated scenarios.
- Self-Assessment Questionnaires: Initial insights into the perceived competencies of healthcare staff. Useful as a starting point for targeted education.
- Peer Reviews: Allows staff to receive constructive feedback from colleagues, illuminating areas for improvement.
- 360-degree Feedback: Incorporates feedback from peers, supervisors, and subordinates, as well as self-assessment for a rounded view of an individual's capabilities.
- Direct Observation: The most effective way to assess competency through direct observation in the clinical setting, providing immediate feedback and guidance.
- Competency Checklists: Systematic evaluation based on industry standards and guidelines.
- KPIs and Performance Metrics: Quantitative data such as response times or patient outcomes, used in conjunction with other assessment methods.
Strategies to Support Healthcare Staff Improve Skills in Identifying and Responding to Patient/Client Deterioration
Staff development is crucial for improving patient outcomes. Below are key strategies to consider:
- Regular Training Sessions: Consistent, scheduled training ensures that skills are kept up-to-date and that new guidelines or procedures are quickly disseminated.
- Simulation-Based Training: Simulated scenarios allow staff to practice identification and response skills in a risk-free environment.
- Mentorship Programs: Pairing less experienced staff with seasoned professionals can fast-track the development of critical skills.
- Feedback Loops: Regular feedback, both positive and constructive, helps staff understand their strengths and areas for improvement.
- Interdisciplinary Training: Collaboration between disciplines (e.g., nursing and physiotherapy) can provide a more holistic approach to patient care.
- Online Learning Modules: Digital resources offer flexibility, allowing staff to learn at their own pace and revisit materials as needed.
- Case Reviews: Regularly reviewing and discussing actual cases can offer practical insights into effective identification and response strategies.
- Quality Improvement Projects: Staff can identify gaps in the existing protocols and work on projects to improve them, thereby learning by doing.
- Resource Availability: Ensure that staff have easy access to up-to-date guidelines, tools, and equipment required for effective patient care.
- Performance Assessments: Regular assessments can track staff competency over time, providing data that can be used to tailor ongoing training.
Sample Training Plan for Identifying and Responding to Patient/Client Deterioration
Using the below staff competency on identifying and responding to patient/client deterioration, a unique training plan can be used to target the lacking skills.
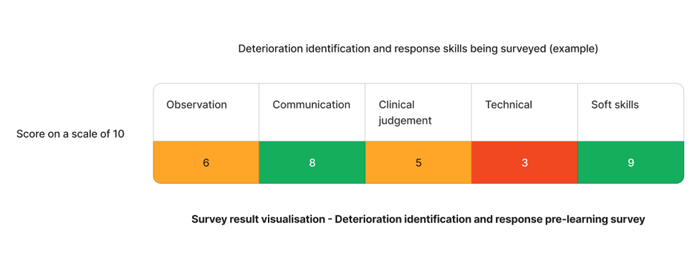
Based on the results - "clinical" and "administrative" skills require action.
Is your current LMS lacking patient deterioration content?
Contact Ausmed today and see how our solutions can help your organisation meet the patient deterioration standard!
Staff Competency Assessment for Patient/Client Deterioration - Example
Understanding the varying competencies your staff have in regards to developing skills on deterioration identification and response will allow you to target your learning and skills development training plans to your organisation's specific needs.
Staff Survey - Identifying and Responding to Patient/Client Deterioration
-
Can you define patient deterioration?
- 1. Yes
- 2. Somewhat
- 3. No
-
What vital signs should be regularly monitored?
- [Answer here]
-
What is the Early Warning Score (EWS)?
- [Answer here]
-
How would you communicate an identified risk to colleagues?
- [Answer here]
-
What would you include in an emergency response plan?
- [Answer here]
-
What are common medications used in emergency response?
- [Answer here]
-
How would you delegate tasks during an emergency?
- [Answer here]
-
What resources would you consult for decision support?
- [Answer here]
-
How confident are you in identifying patient deterioration?
- 1. Not confident at all
- 2. Somewhat confident
- 3. Confident
- 4. Very confident
- 5. Extremely confident
-
How confident are you in responding to patient deterioration?
- 1. Not confident at all
- 2. Somewhat confident
- 3. Confident
- 4. Very confident
- 5. Extremely confident
Conclusion
Understanding and developing comprehensive care plans is a cornerstone for improving patient outcomes. Ensuring your staff are well-equipped with the necessary skills and competencies is the first step towards that.
References
- Stelfox, H.T., Bagshaw, S.M., & Gao, S. (2015). A retrospective cohort study of age-based differences in the care of hospitalized patients with sudden clinical deterioration. Journal of Critical Care
- Gerry, S., Bonnici, T., Birks, J., Kirtley, S., Virdee, PS., Watkinson, PJ., Collins, GS. (2020). Early warning scores for detecting deterioration in adult hospital patients: systematic review and critical appraisal of methodology. The BMJ
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'Recognising and Responding to Acute Deterioration Standard'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 8.05'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 8.10'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 8.11'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 8.12'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 8.13'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Aged Care Quality Standard - Ongoing Assessment - 3.3 (d)'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Stronger Standards, Better Aged Care Program - 3.2.5'


