This article is part of our Training Requirement Series where we provide comprehensive guides to meet the actual training requirements that are often needed/requested of learning and development departments within Australia's healthcare organisations. This series includes both general requirements, such as medicines scope of clinical practice but also focuses on the specific requirements stemming from the NDIS, Aged Care and NSQHS Quality Standards.
Medicines Scope of Clinical Practice in Healthcare Organisations
Developing a comprehensive training program for the Medicines Scope of Clinical Practice within healthcare organisations is pivotal for ensuring safe, effective, and quality patient care. This training requirement outlines the essential components and strategies for learning and development coordinators to establish a robust framework.
What is "Medicines Scope of Clinical Practice"?
The scope of clinical practice for medicine defines the professional activities that a healthcare practitioner is qualified, educated, competent, and authorised to perform. It is a dynamic framework that aligns with evolving healthcare needs, practitioner's expertise, and the organisational context, ensuring patient safety and high-quality care is front of mind.
Examples of Medicines Scope of Clinical Practice
The Medicines Scope of Clinical Practice encompasses a broad range of responsibilities critical to patient care within healthcare organisations. These responsibilities ensure that patients receive safe, effective, and appropriate medication management throughout their care journey. Key aspects of this scope include:.
- Administering medications: This involves the process of evaluating the patient's condition and determining the most appropriate medication to manage their health issues effectively.
- Monitoring patient responses to medications: It's essential for healthcare professionals to identify clinical changes that a patient may be experiencing following the administration of medications.
- Adjusting dosages based on patient condition Depending on the patient's response to the medication, healthcare professionals may need to modify the dosage to achieve the best health outcomes.
- Medication reconciliation: This critical process involves reviewing all the medications a patient is currently taking (prescription, non-prescription, herbal, and supplements) to avoid medication errors such as duplications, omissions, and interactions.
What is the "Medicines Scope of Clinical Practice" Training Requirement?
Under the National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards, particularly within the framework of Action 4.04, healthcare organisations are mandated to delineate a precise scope of clinical practice concerning medicines management. This directive necessitates the formulation of guidelines that outline the roles, responsibilities, and limitations of all staff members engaged in the processes of medication handling, from prescribing to administration and monitoring. The objective of this requirement is to foster an environment of safe and efficacious care by ensuring that each healthcare professional is fully aware of their scope of practice and comptence within the context of medication management.
Relevant Standards
Action 4.04: Medicines scope of clinical practice
The health service organisation has processes to define and verify the scope of clinical practice for prescribing, dispensing and administering medicines for relevant clinicians.
Action 1.23 : Credentialing and scope of clinical practice
The health service organisation has processes to:
- a) Define the scope of clinical practice for clinicians, considering the clinical service capacity of the organisation and clinical services plan
- b) Monitor clinicians’ practices to ensure that they are operating within their designated scope of clinical practice
- c) Review the scope of clinical practice of clinicians periodically and whenever a new clinical service, procedure or technology is introduced or substantially altered
Action 1.24 : Credentialing and scope of clinical practice
The health service organisation has processes to:
- a) Conducts processes to ensure that clinicians are credentialed, where relevant
- b) Monitors and improves the effectiveness of the credentialing process
National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards
Failure to comply with the requirements could lead to an organisation being penalised or reprimanded.
Related Training Requirements Guides
The following Training Requirement guides can be used to support and facilitate the medicines scope of clinical practice training requirement:
Skills Required for the Medicines Scope of Clinical Practice Requirement?
Staff involved in the medicines scope of clinical practice must possess a range of skills to meet this requirement effectively:
- Comprehensive knowledge of pharmacology: This includes an understanding of drug mechanisms, interactions, side effects, and therapeutic uses to ensure safe and effective medication management.
- Understands healthcare organisation's medication management policies: Adherence to the organisation's guidelines and protocols for medication management, prescribing, and administration.
- Communication Skills: It ensures that healthcare professionals can accurately convey and interpret critical information regarding medication use, potential side effects, and any specific instructions that are essential for the patient's understanding and adherence to their treatment plan.
- Ability to assess and monitor patient conditions: Critical in determining the appropriate medication regimens and adjustments based on patient responses and changes in their health status.
- Legal and Ethical Understanding: Awareness of legal responsibilities and ethical considerations is crucial in medication management to ensure compliance with regulations and safeguard patient rights.
- Safe medication administration and error prevention: Proficiency in administering medications accurately and safely, recognizing potential errors, and implementing strategies to prevent them.
- Competency in medication reconciliation and patient education: Ability to review and reconcile all medications a patient is taking and effectively educate patients about their medications, including how to take them correctly and potential side effects.
Assessing Staff Competency in Medicines Scope of Clinical Practice Requirement
Assessment of staff competency is critical to ensure that healthcare professionals are able to manage medications safely and effectively. This can be achieved through:.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular performance evaluations | Periodic assessments of an employee's work performance, focusing on their efficiency, accuracy, and adherence to protocols in medication management. |
| Competency-based assessments | Evaluations designed to measure an individual's skills, knowledge, and ability in specific areas related to medication management, ensuring they meet the required standards. |
| Simulation exercises | Practical training scenarios that mimic real-life situations involving medication administration, allowing staff to practice and hone their skills in a safe environment. |
| Colleague feedback | A process where colleagues provide constructive criticism and feedback on one's performance, particularly in handling medications, to promote learning and improvement. |
Strategies to Support Employees Enhance Skills in the Medicines Scope of Clinical Practice Requirement
To support employees in enhancing their skills, organisations should implement a multi-faceted approach these include:
- Education and training programs: Implementing regular and structured educational initiatives to enhance staff knowledge and skills in medication management, ensuring they are up-to-date with current practices.
- Participation in workshops and seminars: Motivating employees to attend external and internal workshops and seminars that focus on advancements and best practices in medication management.
- Mentorship and peer support systems: Establishing systems where experienced staff mentor newer employees, promoting knowledge sharing and support in handling medications safely and effectively.
- Simulation Exercises: Using realistic scenarios to practice medication documentation, helping staff to apply their knowledge in a controlled environment.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Implementing systems for regular feedback, both formal and informal, to encourage continual learning and improvement.
Skills development Training Plan for Medicines Scope of Clinical Practice Requirement
Developing a detailed training plan is crucial for improving the competencies necessary for proficient management within the scope of clinical practice for medicines. Here is an example plan that delineates an all-encompassing strategy for skill advancement in this area.
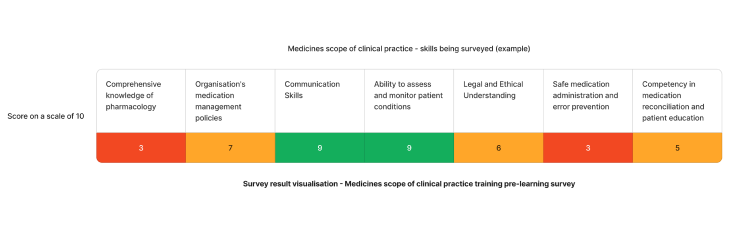
Using the above needs assessment survey as an example - The skills requiring the most attention for providing safe medication management in healthcare is comprehensive knowledge of pharmacology and safe medication administration and error prevention. We can target learning initiatives to fill these gaps to enhance staff competency.
| Quarter | Topics | Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Comprehensive knowledge of pharmacology |
|
| Q2 | Safe medication administration and error prevention |
Need an LMS that can support medicines scope of clinical practice training?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support with your training requirement needs!
Staff Competency Assessment for medicines scopes of clinical practice - Example
Consider the following survey questions to evaluate staffs skills:
Staff Survey - Medicines Scope of Clinical Practice Competency
-
On a scale of 1 to 10, how well do you believe you understand your healthcare organisation's medication management policies?
- [Answer here]
-
How frequently do you participate in simulation exercises to improve your medication administration skills?
- [Answer here]
-
What steps do you take to stay updated on the legal and ethical aspects of medication documentation?
- [Answer here]
-
How effectively are you able to identify and respond to signs of a deteriorating patient ?
- [Answer here]
Conclusion
In conclusion, establishing a robust framework for the Medicines Scope of Clinical Practice within healthcare organisations is pivotal to ensuring safe, effective, and quality patient care. By focusing on the development of a structured training plan, regular competency assessments, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, healthcare professionals can significantly enhance their skills in medication management. Ultimately, the goal is to equip healthcare workers with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate the complexities of medication documentation and administration, thereby minimising errors and improving patient outcomes. Through collective effort and dedication to professional development, healthcare organisations can achieve excellence in medicines management and set a benchmark for quality care in the industry.
References
- Fong, J, Cashin, A & Buckley, T, 2020. Models of prescribing, scope of practice, and medicines prescribed, a survey of nurse practitioners, Journal of Advanced Nursing, vol.76 no.9, pp.2311-2322.
- Queensland Health, 2023,'Credentialing and defining the scope of clinical practice',
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2024. 'Medication Safety Standard'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2024. 'NSQHS Action 4.04'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2024. 'NSQHS Action 1.23'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2024. 'NSQHS Action 1.24'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2024. 'NSQHS Credentialing health practitioners and defining their scope of clinical practice: A guide for managers and practitioners


