This article is part of our Training Requirement Series where we provide comprehensive guides to meet the actual training requirements that are often needed/requested of learning and development departments within Australia's healthcare organisations. This series includes both general requirements, such as medicine information and decision support tools, but also focuses on the specific requirements stemming from the NDIS, Aged Care and NSQHS Quality Standards.
Developing a Training Program for Medicine Information and Decision Support Tools in Healthcare Organisations
Medicine information and decision support tools are essential for the safe and effective management of medications within healthcare settings. This article outlines the development of a training program for these tools, focusing on the requirements of the National Safety and Quality Health Service Standards, particularly Standard 4 'The Medication Safety Standards' and Standard 5 in the Strengthened Standards related to the 'Safety and Quality Use of Medicines.
What are Medicine Information and Decision Support Tools?
Medicine information and decision support tools are integral components in the healthcare system, designed to support clinical decisions related to medication use. These tools encompass a wide range of applications, from electronic prescribing and medication databases to advanced clinical algorithms that offer personalised drug therapy recommendations based on patient-specific data. By integrating evidence-based guidelines and real-time patient information, these tools facilitate informed decision-making, ensuring that medication choices are aligned with the latest clinical standards and patient safety requirements. Furthermore, they play a pivotal role in educating healthcare professionals about the safe and effective use of medications, thereby enhancing the overall quality of care provided to patients.
Examples of Medicine Information and Decision Support Tools
The landscape of medicine information and decision support tools is diverse, encompassing various technologies that enhance medication safety and efficacy.
- Electronic Medication Management Systems (eMMS)
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
- Drug Reference Databases
- Medication Reconciliation Tools
What is the Medicine Information and Decision Support Tools Requirement?
The requirement involves ensuring healthcare staff have access to and are trained in using these tools to support the safe and quality use of medicines, aligning with specific actions outlined in the National Safety and Quality Health Service Standards.
Relevant Standards
Action 4.01 states Integrating clinical governance :
Clinicians use the safety and quality systems from the Clinical Governance Standard when:
- Implementing policies and procedures for medication management
- Managing risks associated with medication management
- Identifying training requirements for medication management
Action 4.02 states Applying quality improvement systems :
The health service organisation applies the quality improvement system from the Clinical Governance Standard when:
- Monitoring the effectiveness and performance of medication management
- Implementing strategies to improve medication management outcomes and associated processes
- Reporting on outcomes for medication management
Action 4.13 states Information and decision support tools for medicines :
The health service organisation ensures that information and decision-support tools for medicines are available to clinicians.
Action 4.14 states Safe and secure storage and distribution of medicines:
The health service organisation complies with manufacturers’ directions, legislation, and jurisdictional requirements for the:
- Safe and secure storage and distribution of medicines
- Storage of temperature-sensitive medicines and cold chain management
- Disposal of unused, unwanted or expired medicines
National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards
The provider implements a system for the safe and quality use of medicines, including processes to ensure:
- a) access to medicines-related information for older people, workers and health professionals
- b) access for health professionals and others caring for an older person to the older person’s up-to-date medicines list and other supporting information at transitions of care
- c) safe administration including assessing the older person’s swallowing ability, determining suitability of crushing medicines and providing alternative safe formulations when required
- d) minimal interruptions to the administration of prescribed medicines including supporting access to medicines when an older person is prescribed a new medicine or an urgent change to their medicine
- e) documentation of a current, accurate and reliable record of all medicines and the clinical reasons for the treatment, including pro re nata (PRN) medicines
- f) support remote access for prescribing.
The provider regularly reviews and improves the effectiveness of the system for the safe and quality use of medicines.
Strengthened Quality Standards framework analysis - Aged Care Quality Standards
Failure to comply with the requirements could lead to an organisation being penalised or reprimanded.
Related Training Requirements Guides
The following Training Requirement guides can be used to support and facilitate the medication review training requirement:
What Skills do Staff Need for Using Medicine Information and Decision Support Tools?
Staff need a range of skills to effectively use these tools, including:
| Skill | Key Elements |
|---|---|
| Technical proficiency | Staff should be skilled in technical proficiency in using electronic health records and medication management systems. |
| Communication | Staff must be able to effectively convey their findings and recommendations to other members of the healthcare team. |
| Attention to detail | Staff must be meticulous in their review of medication regimens, ensuring that nothing is missed and that all potential issues are identified and addressed. |
| Analytical skills | Staff must be able to analyse a patient’s medication regimen critically to identify potential issues. |
| Critical Thinking | Staff must be able evaluate information critically and make informed decisions during the medication review process. |
| Continuous learning and improvement | The field of medicine is constantly evolving, and staff must be proactive in staying up-to-date with the latest research, treatment guidelines, and best practices in medication management. |
How to Assess Staff Competency in Medicine Information and Decision Support Tools
Assessing staff competency involves a combination of methods to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of their skills and knowledge in using these tools.
- Direct observation of tool usage in practice: This approach involves watching employees use the tools in their actual work environment. It allows for an assessment of how effectively and safely staff apply their knowledge of the tools in real-life situations, identifying both proficiency and areas needing improvement.
- Self-assessment questionnaires: These are surveys that staff complete, reflecting on their own use and understanding of the tools. This method helps individuals recognize their strengths and identify areas where they may need further training or support.
- Practical tests and simulations: Through simulations or controlled practical exams, staff can demonstrate their ability to use these tools in scenarios that mimic real-world challenges. This method tests both theoretical knowledge and practical skills in a safe, learning-focused setting. .
- Feedback from peers and supervisors: Gathering input from colleagues and supervisors provides multifaceted perspectives on an individual's use of medicine information and decision support tools. This feedback can highlight areas of excellence and opportunities for growth, fostering a culture of continuous learning and development..
- Regular Audits: Conduct these on medication management practices, ensuring adherence to best practices and identifying any systemic issues.
Strategies to Support Employees Enhance Skills in Medicine Information and Decision Support Tools
To support skill enhancement, consider the following strategies:
- Regular training sessions:These structured educational experiences provide staff with up-to-date information and hands-on practice with medicine information and decision support tools. By regularly participating in these sessions, employees can keep abreast of the latest developments and best practices in medication management.
- Practical Experience:Pair less experienced staff with more knowledgeable colleagues or supervisors who provide real-time guidance and support.
- Continuous learning opportunities:Providing staff with access to a wealth of online educational materials, such as tutorials, webinars, and courses, enables them to learn at their own pace and according to their individual learning needs.
- Regular Feedback Sessions: Ensure staff are aware of their strengths and areas for improvement.
- Interdisciplinary Learning Opportunities: Promote collaboration with colleagues from different disciplines, fostering a holistic approach to patient care.
Skills Development Training Plan for Medicine Information and Decision Support Tools
The proficiency of staff in maintaining safety around medication safety should be bolstered by a robust training program, which is designed after identifying skill gaps through a needs assessments.
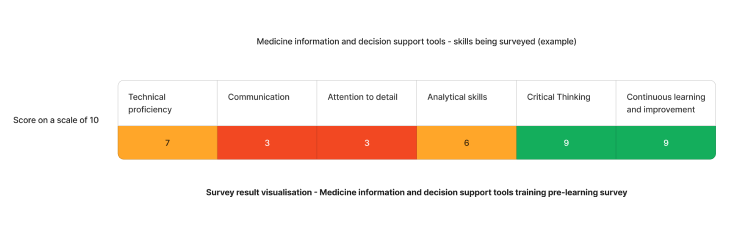
Using the above needs assessment survey as an example - The medicine information and decision support that require the most attention are attention to detail and communication skills. We can target learning initiatives to fill these gaps to enhance staff competency.
Need an LMS that can support Medicine Information and Decision Support Tools training?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support with your medication review training requirements!
Staff Competency Assessment for Medicine Information and Decision Support Tools - Example
To assess a staff member's competence in Medicine Information and Decision Support Tools, consider the following survey questions:
Staff Survey - Medicine Information and Decision Support Tools Competency
-
What challenges, if any, have you encountered while using medicine information and decision support tools in your practice?
- [Answer here]
-
How often do you use these tools for medication decisions?
- [Answer here]
-
How well do the current training programs on medicine tools help you get better at your job?
- [Answer here]
-
How do you involve other healthcare professionals in the medication review process?
- [Answer here]
-
How do you communicate medication changes to patients and their families?
- [Answer here]
-
How do you stay up-to-date with current best practices in medication management?
- [Answer here]
-
Can you provide an example of a challenging medication review you have conducted and how you handled it?
- [Answer here]
-
How do you assess the effectiveness of a medication regimen?
- [Answer here]
Conclusion
In conclusion, the development and implementation of a comprehensive training program for medicine information and decision support tools are essential for advancing patient safety and care quality in healthcare organisations. By aligning with the National Safety and Quality Health Service Standards, and focusing on the critical areas of medication safety and quality use of medicines, healthcare providers can ensure their staff are well-equipped to handle the complexities of modern medication management. The integration of various assessment methods, alongside continuous learning and support strategies, establishes a robust foundation for skill enhancement. Ultimately, this guide serves as a helpful tool for learning and development coordinators to create an environment where the safe and effective use of medicine information and decision support tools is a standard practice, contributing to the overall improvement of healthcare outcomes.
References
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2024, National Safety and Quality Health Service Standards. 'Standards'
- Sutton, RT, Pincock, D, Baumgart, DC, Sadowski, DC, Fedorak, RN, Kroeker, KI 2020, ' An overview of clinical decision support systems: benefits, risks, and strategies for success' npj Digital Medicine, vol. 3, no. 17, pp. 1-10. doi: org/10.1038/s41746-020-0221-y.
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2024. 'NSQHS Action 4.01'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2024. 'NSQHS Action 4.02'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2024. 'NSQHS Action 4.13'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2024. 'NSQHS Action 4.14'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2024. 'Stronger Standards, Better Aged Care Program - Action 5.3.1'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2024. 'Stronger Standards, Better Aged Care Program - Action 5.3.6'


