This article is part of our Training Requirement Series, where we provide comprehensive guides to meet the actual training requirements that are often needed/requested of learning and development departments within Australia's healthcare organisations. This series includes both general requirements, such as comprehensive care planning, but also focuses on the specific requirements stemming from the NDIS, Aged Care and NSQHS Quality Standards.
What is "Comprehensive Care Planning"?
Comprehensive care planning is an essential approach in healthcare that addresses the multifaceted needs of patients. It involves creating personalised care strategies that account for the physical, psychological, social, and spiritual well-being of individuals. In this process, healthcare professionals from various disciplines collaborate to develop a care plan that evolves with the patient's needs and circumstances.
Why is Comprehensive Care Planning Important?
- Patient-Centred Care: Emphasises the importance of incorporating patient preferences and values into their care.
- Improved Health Outcomes: Holistic care approaches contribute to more effective and comprehensive patient health management.
- Efficiency and Effectiveness: Streamlines care processes and reduces unnecessary interventions, leading to better resource utilisation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meets the standards set by healthcare regulatory bodies and ensures quality care.
What is the "Comprehensive Care Planning" Training Requirement?
Training for comprehensive care planning is integral to meeting healthcare standards. It encompasses a range of topics, including understanding diverse patient needs, mastering effective communication techniques, collaborating in multidisciplinary teams, and staying informed about legal and ethical considerations in patient care.
Relevant Standards
Processes are in place that are relevant to patients using services provided:
- For integrated and timely screening and assessment
- That can identify risks of harm (as noted in the Minimising patient harm criteria)
Systems are in place to support patients of Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander origin by:
- Developing policies, protocols and processes to confirm patient identity
- Training staff to build competence in diverse population groups
- Including Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander identifiers in administration information and data
- Monitoring and reporting on these strategies
Processes are developed to support patients in documenting clear advance care plans
Systems are in place to support:
- Clinicians in using local and organisational systems to document findings from screening and assessment
- Involvement of clinicians in evaluating and improving documentation processes
Clinicians engage in collaborative decision-making to create and record a detailed, personalised plan that:
- Tackles the importance and intricacy of the patient's health conditions and potential risks
- Establishes consensus on objectives and measures for the patient's treatment and care
- Specifies which individuals the patient wishes to include in discussions and decisions about their care
- Initiates planning for discharge at the onset of the care episode
- Incorporates a strategy for referring to subsequent services when suitable and accessible
- Aligns with established best practices and current evidence.
National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards
Requirement 2 (3) (b): Comprehensive care planning
(b) Assessment and planning is used to identify and address the client's current needs, goals and preferences, (including advance care planning and end of life planning if the consumer wishes)
Action 5.4.1: Comprehensive care planning:
The provider implements an assessment and planning system that supports partnering with the older person, families, carers and others to set goals of care and support decision-making.
Action 5.4.2: Comprehensive care assessment:
When care begins, the provider performs a clinical assessment including:
- a. a comprehensive medical assessment with a General Practitioner
- b. collaboration with health professionals who know the older person
- c. identifying, documenting and planning for clinical risks, acute conditions and exacerbations of chronic conditions
- d. identifying an older person’s level of clinical frailty and communication barriers and planning clinical care to optimise the older person’s quality of life, reablement and maintenance of function.
- e. referring and facilitating access to medical, rehabilitation, allied health, specialist nursing and advisory services to address the older person’s clinical needs
- f. identifying and providing access to the equipment, aids, devices and products required by the older person.
Action 5.4.3: Comprehensive care plans and documentation:
The provider uses the care and services plan required (as part of Standard 3) to document the outcomes of clinical assessments, treatment and agreed goals of care.
Strengthened Quality Standards framework analysis - Aged Care Quality Standards
Failure to comply with the requirements could lead to an organisation being penalised or reprimanded.
Related Training Requirements Guides
The following Training Requirement guides can be used to support and facilitate the comprehensive care planning training requirement:
What Skills Do Staff Need for Comprehensive Care Planning?
Healthcare professionals involved in care planning need a diverse skill set to effectively create and implement patient-centered care plans. These skills are not only essential for quality patient care but also for meeting regulatory and organisational standards.
| Skill | Description |
|---|---|
| Communication Skills | Essential for clear and empathetic interactions with patients and for effective teamwork. |
| Critical Thinking | Enables professionals to assess patient needs accurately and develop suitable care plans. |
| Empathy and Sensitivity | Fundamental for understanding patient experiences and respecting their preferences and values. |
| Knowledge of Healthcare Policies | Understanding relevant healthcare standards, guidelines, and regulations is critical for compliance and quality care. |
| Interdisciplinary Collaboration | Comprehensive care often involves a team of professionals from various disciplines. Collaborating effectively ensures that all aspects of a patient's care are addressed. |
| Adaptability and Flexibility | Professionals need to adjust care plans efficiently and responsively, ensuring that they continually meet the evolving needs of patients. |
How to Assess Staff Competency in Comprehensive Care Planning
Evaluating the competency of staff in comprehensive care planning is crucial for ensuring that they are equipped to provide high-quality care. This section outlines various methods to assess staff capabilities effectively.
- Direct Observation: Supervisors can gauge the proficiency of staff in real-time during patient interactions and care planning sessions.
- Case Studies and Role Plays: These simulate real-world scenarios, allowing staff to demonstrate their skills in a controlled environment.
- Feedback from Patients and Families: Collecting feedback provides insights into the staff's ability to meet patient needs and preferences.
Strategies to Support Healthcare Staff Develop Skills in Comprehensive Care Planning
Developing the skills required for comprehensive care planning is an ongoing process. This section highlights various strategies that can be employed to enhance staff capabilities in this area.
- Regular Training Workshops: Organise workshops to cover different aspects of care planning and to update staff on the latest guidelines and practices.
- Mentoring Programs: Pairing less experienced staff with mentors can facilitate knowledge transfer and provide support in skill development.
- Performance Feedback: Regular, constructive feedback helps staff identify areas for improvement and track their progress over time.
Sample Training Plan for the Comprehensive Care Planning Requirement
The ability of staff to perform comprehensive care planning is extremely important to all aspects of healthcare.
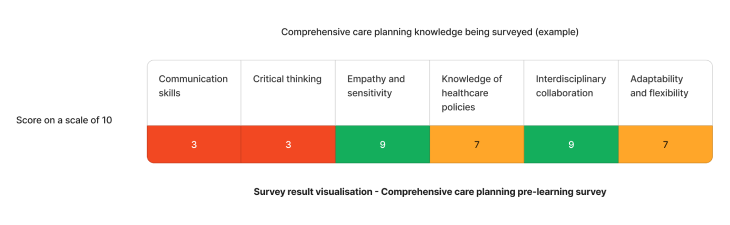
Using the above needs assessment survey as an example - The skills needing most attention for effective comprehensive care planning are communication and critical thinking skills. We can target learning initiatives to fill these gaps to enhance staff competency.
| Quarter | Topics | Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Communication | |
| Q1 | Critical Thinking |
Need an LMS that can support comprehensive care planning training?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support with your training requirements needs!
Staff Competency Assessment for Comprehensive Care Planning - Example
Consider the following survey questions to evaluate staff comprehensive care planning skills:
Staff Survey - Comprehensive Care Planning Competency
-
How do you determine a patient's care needs?
- [Answer here]
-
Describe how you would handle conflicting patient and family preferences.
- [Answer here]
-
How do you stay updated with the latest care planning guidelines?
- [Answer here]
-
Can you give an example of a multidisciplinary approach in care planning?
- [Answer here]
-
How do you measure the effectiveness of a care plan?
- [Answer here]
-
Describe a situation where you adapted a care plan based on patient feedback.
- [Answer here]
Conclusion
Comprehensive care planning is an integral component of quality healthcare delivery. By focusing on the development and assessment of essential skills, healthcare organisations can ensure their staff are well-prepared to create and implement effective care plans, leading to improved patient outcomes and satisfaction.
References
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS - Comprehensive Care Standard'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 5.07'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 5.08'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 5.09'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 5.12'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 5.13'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Requirement 2 (3) (b)'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Stronger Standards, Better Aged Care Program - Action 5.4.1 - 5.4.3'


