This article is part of our Training Requirement Series where we provide comprehensive guides to meet the actual training requirements that are often needed/requested of learning and development departments within Australia's healthcare organisations. This series includes both general requirements, such as integrating clinical governance but also focuses on the specific requirements stemming from the NDIS, Aged Care and NSQHS Quality Standards.
What is Clinical Governance?
Clinical governance is a systematic approach to maintaining and improving the quality of patient care within a healthcare setting. This concept encompasses a range of activities and responsibilities designed to ensure that patients receive the highest standard of care possible.
Clinical governance is integral to modern healthcare systems, providing a framework that helps healthcare organisations and professionals to be accountable for continually improving the quality of their services and safeguarding high standards of care.
What is Integrating Clinical Governance?
Integrating clinical governance involves embedding a systematic approach within healthcare organisations to maintain and improve the quality of patient care. It aligns with standards set by the National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) - Actions 2.01, 3.01, 3.02, 4.01, 5.01, 7.01, Aged Care Standards - Requirement 8.3(e), and Strengthened Aged Care Standards - Actions 5.1.1, 5.1.2. This integration ensures that organisations continually evaluate, monitor, and improve their health services.
The Importance of Integrating Clinical Governance

The integration of clinical governance is crucial for several reasons. It ensures patient safety, improves the quality of healthcare services, facilitates compliance with regulatory standards, and promotes a culture of continuous improvement. By embedding these practices, healthcare organisations can achieve better patient outcomes, enhance staff morale, and maintain high standards of care.
Integrating clinical governance into healthcare organisations is crucial for several key reasons:
- Patient Safety and Quality of Care: Central to clinical governance is the improvement of patient safety and care quality. This approach reduces medical errors and ensures care is safe, effective, and patient-centred.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards: It ensures adherence to healthcare regulations and standards, maintaining professional practices at the highest level.
- Continuous Improvement and Innovation: Clinical governance fosters a culture of continuous learning and adaptation, vital in the ever-evolving medical field.
- Enhanced Reputation and Public Trust: Effective governance builds trust in healthcare services, enhancing the organisation's reputation and attracting skilled professionals.
- Efficient Resource Management: It leads to optimal resource use, reducing costs associated with medical errors and enabling better patient care investments.
- Empowerment of Healthcare Professionals: Involving staff in governance processes boosts engagement, responsibility, and job satisfaction, positively impacting patient care.
- Legal and Ethical Responsibility: Integrating clinical governance fulfills ethical obligations, reflecting a commitment to 'do no harm' in healthcare.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: This approach uses data to inform decisions, ensuring they are based on evidence and best practices.
What is the "Integrating Clinical Governance" Training Requirement?
Training in clinical governance is vital for all healthcare staff. It involves understanding the frameworks, policies, and practices that underpin the delivery of high-quality healthcare. Training must cover the relevant NSQHS and Aged Care Standards to ensure compliance and effective implementation of clinical governance practices.
Relevant Standards
Action 2.01: Integrating clinical governance - Partnering with Consumers Standard
Clinicians use the safety and quality systems from the Clinical Governance Standard when:
- Implementing policies and procedures for partnering with consumers
- Managing risks associated with partnering with consumers
- Identifying training requirements for partnering with consumers
Action 3.01: Integrating clinical governance - Preventing and Controlling Infections Standard
The workforce uses the safety and quality systems from the Clinical Governance Standard when:
- Implementing policies and procedures for infection prevention and control
- Identifying and managing risks associated with infections
- Implementing policies and procedures for antimicrobial stewardship
- Identifying and managing antimicrobial stewardship risks
Action 3.02: Integrating clinical governance - Preventing and Controlling Infections Standard
The health service organisation:
- Establishes multidisciplinary teams to identify and manage risks associated with infections using the hierarchy of controls in conjunction with infection prevention and control systems
- Identifies requirements for, and provides the workforce with, access to training to prevent and control infections
- Has processes to ensure that the workforce has the capacity, skills and access to equipment to implement systems to prevent and control infections
- Establishes multidisciplinary teams, or processes, to promote effective antimicrobial stewardship
- Identifies requirements for, and provides access to, training to support the workforce to conduct antimicrobial stewardship activities
- Has processes to ensure that the workforce has the capacity and skills to implement antimicrobial stewardship
- Plans for public health and pandemic risks
Action 4.01: Integrating clinical governance - Medication Safety Standard
Clinicians use the safety and quality systems from the Clinical Governance Standard when:
- Implementing policies and procedures for medication management
- Managing risks associated with medication management
- Identifying training requirements for medication management
Action 5.01: Integrating clinical governance - Comprehensive Care Standard
Clinicians use the safety and quality systems from the Clinical Governance Standard when:
- Implementing policies and procedures for comprehensive care
- Managing risks associated with comprehensive care
- Identifying training requirements to deliver comprehensive care
Action 7.01: Integrating clinical governance - Blood Management Standard
Clinicians use the safety and quality systems from the Clinical Governance Standard when:
- Implementing policies and procedures for blood management
- Managing risks associated with blood management
- Identifying training requirements for blood management
National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards
Requirement 8.3 (e): Assesment and planning
Where clinical care is provided – a clinical governance framework is needed.
Action 5.1.1: Governing body's requirements
The governing body:
- Sets priorities and strategic directions for safe and quality clinical care and ensures that these are communicated effectively to workers and older people
- Endorses the clinical governance framework
- Monitors the safety and quality of clinical systems and performance
Action 5.1.2: Clinical governance frameworks
The provider implements the clinical governance framework as part of corporate governance, to drive safety and quality using:
- Feedback and information on experiences of older people, family, carers and workers
- Analysis of clinical safety and quality indicator data, including the mandatory Quality Indicator Program
- Contemporary, evidence based practice.
Strengthened Quality Standards framework analysis - Aged Care Quality Standards
Failure to comply with the requirements could lead to an organisation being penalised or reprimanded.
Staff Skills Required for Integrating Clinical Governance
Before diving into the specific skills, it's essential to understand that successful integration of clinical governance requires a multifaceted skill set. These skills range from analytical abilities to effective communication and leadership. The following list highlights the key competencies needed:
| Skill | Description |
|---|---|
| Risk Management | Ability to identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks in healthcare settings, ensuring patient safety and a secure environment. |
| Quality Improvement | Proficiency in using quality improvement methodologies, conducting audits, analysing data, and implementing changes to enhance care quality. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Knowledge of healthcare regulations and standards, and the ability to apply these in practice to ensure organisational compliance. |
| Leadership | Skills in inspiring and leading teams, managing change, and promoting a culture of safety and continuous improvement in healthcare settings. |
| Data Analysis | Competence in collecting, analysing, and using healthcare data to inform decisions and drive improvements in patient care. |
How to Assess Staff Competency in Integrating Clinical Governance
Assessing staff competency is a critical step in ensuring effective clinical governance. This assessment should be comprehensive, covering various aspects of clinical governance skills. The following table provides a structured approach for this assessment.
- Direct Observation: Supervisors or peers observe interactions with patients, focusing on the application of key skills.
- Feedback from Patients: Collecting feedback through surveys or interviews to gauge patient satisfaction and staff effectiveness.
- Self-Assessment: Encouraging staff to reflect on their skills and identify areas for improvement.
- Role-Playing Exercises: Simulating scenarios where staff can demonstrate their ability to partner with patients.
- Knowledge Tests: Assessing understanding of best practices and policies related to patient partnership.
Strategies to Support Healthcare Staff Develop Skills in Integrating Clinical Governance
Enhancing skills in clinical governance requires a strategic approach. Employees should be supported through various methods to develop their competencies effectively. The strategies listed below provide a structured framework for skill development:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Continuous Training | Regular workshops and seminars to update skills in line with evolving standards and practices. |
| Mentoring and Peer Support | Pairing less experienced staff with seasoned professionals for guidance and knowledge sharing. |
| Performance Feedback | Regular reviews and constructive feedback on performance related to clinical governance tasks. |
| Simulation Exercises | Hands-on simulations to practice real-life scenarios and decision-making in clinical governance. |
| Online Learning Modules | Utilising digital platforms for flexible and accessible learning opportunities. |
Sample Training Plan for the Integrating Clinical Governance Requirement
A well-structured training plan is instrumental in developing the necessary skills for effective clinical governance. The following table outlines a sample training plan that can be adapted to suit specific organisational needs.
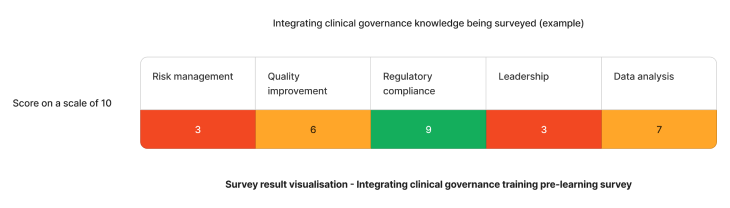
Using the above needs assessment survey as an example - The skill requiring the most attention for integrating clinical governance are empathy and compassion and conflict resolution. We can target learning initiatives to fill these gaps to enhance staff competency.
| Quarter | Topics | Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Risk management | |
| Q1 | Leadership |
|
Need an LMS that can support staff with integrating clinical governance?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support with your training requirement needs!
Staff Competency Assessment for Integrating Clinical Governance - Example
To evaluate an individual's skills in operating integrating clinical governance, consider using these survey questions:
Staff Survey - Integrating Clinical Governance Competency
-
How confident are you in identifying and managing risks in a healthcare setting?
- [Answer here]
-
Can you describe a situation where you successfully applied quality improvement techniques?
- [Answer here]
-
How familiar are you with the NSQHS and Aged Care Standards relevant to clinical governance?
- [Answer here]
-
Describe an instance where you led a team to implement a clinical governance initiative.
- [Answer here]
-
How proficient are you in analysing healthcare data to inform decision-making?
- [Answer here]
Conclusion
Integrating clinical governance into healthcare organisations is a multifaceted process requiring a dedicated approach to training and skill development. By understanding the importance of this integration, identifying the required skills, assessing staff competencies, and implementing effective strategies for skill enhancement, healthcare organisations can ensure the delivery of high-quality, safe, and efficient patient care. Regular assessment through surveys and feedback will help in continuously improving these practices, thus upholding the highest standards in healthcare delivery.
References
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 2.01'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 3.01'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 4.01'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 5.01'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 7.01'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. Aged Care Quality Standards, 'Requirement 8.3(e)'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Stronger Standards, Better Aged Care Program - Action 5.1.1-5.1.2'


