This article is part of our Training Requirement Series where we provide comprehensive guides to meet the actual training requirements that are often needed/requested of learning and development departments within Australia's healthcare organisations. This series includes both general requirements, such as clinical assessment, but also focuses on the specific requirements stemming from the NDIS, Aged Care and NSQHS Quality Standards.
What is Clinical Assessment?
Clinical assessment is a multifaceted process that serves as the cornerstone for healthcare provision. It involves the systematic evaluation of a patient's medical history, physiological symptoms, and psychological well-being. The aim is to facilitate accurate diagnoses and to develop appropriate treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs (Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care, 2023).
Why is Clinical Assessment Important?
Without health practitioners performing clinical assessments they are unable to identify the specific care requirements for their patients. These assessments can be the difference between comfort and discomfort in care, to life or death of patients.
What is the Clinical Assessment Training Requirement?
Healthcare staff, especially those in aged care, public and private hospitals, and disability care settings, are required by NSQHS - 5 - Action 5.11, Aged Care Standards - 2.3(b), and Strengthened Aged Care Standards - 3.1.1, to undergo formal training in clinical assessment. The aim is to guarantee that healthcare practitioners possess the essential skills and knowledge to administer accurate and consistent assessments. This requirement aims to improve the standard of care provided and ensure compliance with national regulations (Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2020).
Relevant Standards
Action 5.11: Clinical assessment
- Clinicians need to comprehensively assess the conditions and risks identified through the screening process of patients
National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards
- (b) Assessment and planning is used to identify and addresses the client's current needs, goals and preferences, (including advance care planning and end of life planning if the consumer wishes)
Action 3.1.1: Systems of assessment:
- a) To identify and record the goals, preferences and needs of the older person
- b) To identify safety risks of client well-being and define strategies to mitigate these risks
- c) To support preventative care to reinforce quality of life, reablement, and maintaining their current function
- d) To involve the relevant health professionals where necessary
- e) To inform and address quality care and services
Strengthened Quality Standards framework analysis - Aged Care Quality Standards
Failure to comply with the requirements could lead to an organisation being penalised or reprimanded.
Clinical Assessment Skills Required for Healthcare Staff
As healthcare professionals aim to offer top-notch patient care, a robust understanding of nutrition and hydration is non-negotiable. While earlier we discussed a variety of skills including menu development, this piece will explore additional competencies required for excelling in nutrition and hydration management. These are crucial across various healthcare settings, including aged care, public and private hospitals, and disability care facilities.
| Skill | Key Elements |
|---|---|
| Observation Skills for Patient Examination |
Observation skills are vital for assessing a patient's physical condition. This includes evaluating skin colour, respiratory rate, and other visual cues that may indicate health issues. |
| Communication Skills |
Practitioners need to be able to ask appropriate questions and interpret the responses to build a comprehensive medical history. |
| Analytical Thinking for Diagnosis and Care Planning |
Staff must critically evaluate all collected data to make accurate diagnoses and formulate suitable care plans. |
| Technical Skills to Perform Tests and Measurements |
Practitioners must be proficient in using medical instruments for tests such as blood pressure measurement, glucose tests, and other diagnostic procedures. |
How to Assess Staff Competency in Clinical Assessment
Ensuring that healthcare staff are competent in clinical assessment is a key component of maintaining high-quality care. To implement an effective competency assessment program, healthcare organisations can adopt a multi-dimensional approach that considers both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Here are some methods commonly used to assess staff competency:
Methods of Assessing Staff Competency in Clinical Assessment
Staff competency can be assessed in the following methods:
- Written Examinations: A written exam can be used to gauge the theoretical understanding staff have about clinical assessments. The exam can include multiple-choice questions, case studies, and even short essays to test knowledge on essential topics such as patient history taking, physiological measurements, and diagnostic criteria (NDIS, 2021).
- Practical Demonstrations: Healthcare staff should demonstrate their clinical assessment skills in a controlled environment, such as a simulation lab. These demonstrations can be conducted using mannequins, computer simulations, or even role-playing with other staff members. They offer an excellent opportunity to assess hands-on skills in real-time scenarios.
- Simulated Patient Scenarios: Simulated or standardized patient encounters offer a realistic setting to test both communication and clinical skills. Trained actors or actual patients can be used to simulate specific clinical situations, allowing the staff to be evaluated on their patient interaction and diagnostic skills.
- Peer Reviews: Peer assessment can offer valuable insights into a healthcare worker's competency. Colleagues can evaluate each other's skills and knowledge in a day-to-day working environment, providing constructive feedback for improvement.
- Performance Metrics: Key performance indicators, such as accuracy in diagnosis and patient satisfaction scores, can be used to objectively evaluate a healthcare worker's performance over a specific period. These metrics can be part of an annual review or used in ongoing performance evaluations.
- Self-Assessment: Encouraging healthcare practitioners to conduct self-assessments can also be beneficial. These allow individuals to reflect on their own strengths and areas for improvement, offering a personal perspective that can be compared with other forms of evaluation.
Strategies to Support Healthcare Staff Improve Clinical Assessment Skills
Develop customised training programs that are aligned with your healthcare setting. This would include hands-on training, workshops, and e-learning modules. Using your Learning Management System (LMS) can make tracking and assessment easier.
Given the importance of polcies and procedures, specified training and strategies must be facilitated in order to develop staff competency, adhere to the requirement set out by the NSQHS and the Aged Care Quality and Safety Commiion.
- On-the-job Training and Mentorship: New staff members can shadow experienced clinicians to gain hands-on experience.
- Workshops and Seminars: These provide opportunities for staff to learn new methodologies and updates in clinical assessment.
- Online Educational Modules: Online platforms can offer flexibility, allowing staff to learn at their own pace.
- Regular Feedback and Assessments: Continuous feedback loops through assessments and appraisals help staff identify and improve weaknesses.
Sample Training Plan for the Clinical Assessment Training Requirement
Ensuring staff are competent in policy and procedures skills and knowledge is vital for your organisation to remain compliant to the Standards. Below is an sample training plan that aligns with Australian standards such as the Aged Care Standards, and NSQHS - based on a mock competency assessment survey.
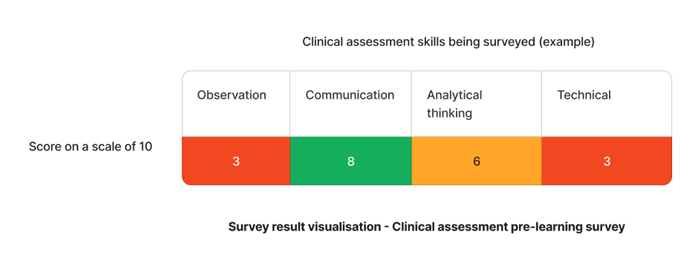
Using the above image as an example - The skills that requires the most attention are observation and technical skills. We can target learning initiatives to fill these gaps to drive clinical staff competency.
| Quarter | Topics | Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Technical skills development |
|
| Q2 | Observation skills development |
Need clinical assessment training for your organisation?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support with your clinical assessment requirements!
Staff Competency Assessment for Clinical Assessment - Example
The following is an example survey that learning and development coordinators may use to asses staff competency on clinical assessment.
Staff Survey - Clinical Assessment Competency
-
How confident do you feel in conducting a complete clinical assessment?
- 1. Not confident at all
- 2. Somewhat confident
- 3. Confident
- 4. Very confident
- 5. Extremely confident
-
Can you explain the steps involved in a clinical assessment?
- [Answer here]
-
How would you rate your communication skills during patient interviews? (Scale of 1-10)
- [Answer here]
-
How often do you update your knowledge on clinical assessment techniques?
- 1. Not often at all
- 2. Somewhat often
- 3. Often
- 4. Very often
- 5. Extremely often
-
Can you perform basic clinical tests and measurements accurately?
- 1. Yes
- 2. Somewhat
- 3. No
Conclusion
In conclusion, clinical assessments are integral to healthcare provision and staff training in this domain is crucial. The article outlines the importance of clinical assessments, requisite skills for healthcare workers, methods for competency assessment, and strategies for skill development, all geared towards improving patient outcomes and complying with Australian healthcare standards.
References
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'NSQHS Comprehensive Care Standard'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 5.11 - Clinical Assessment'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Aged Care Quality Standard - Ongoing Assessment - 2.3 (b)'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Stronger Standards, Better Aged Care Program - 3.1.1'


