This article is part of our Training Requirement Series where we provide comprehensive guides to meet the actual training requirements that are often needed/requested of learning and development departments within Australia's healthcare organisations. This series includes both general requirements, such as antimicrobial stewardship, but also focuses on the specific requirements stemming from the NDIS, Aged Care and NSQHS Quality Standards.
What is Antimicrobial Stewardship?
Antimicrobial stewardship is a vital practice within healthcare organisations. It involves the responsible use of antimicrobial agents to ensure optimal patient outcomes while minimising the development of antimicrobial resistance. This practice is crucial to combat infections effectively.
What is the Antimicrobial Stewardship Training Requirement?
The training requirement for antimicrobial stewardship is outlined in NSQHS Action 3.18, Action 3.19, Aged Care Quality Standards Requirement 3.3(g), and Strengthened Aged Care Standards Action 5.2.1. Healthcare staff must be adequately trained to understand the principles of antimicrobial stewardship, including the appropriate use of antibiotics, infection control, and surveillance.
Relevant Standards
Action 3.18: Antimicrobial stewardship program
Developing a program that:
- Integrate a comprehensive antimicrobial stewardship policy into the organisation's infection prevention strategy.
- Offer access to current, evidence-based Australian Therapeutic Guidelines for antimicrobial prescribing, and promote their utilisation.
- Maintain an antimicrobial formulary that aligns with current evidence-based Australian Therapeutic Guidelines, complete with restriction rules and approval processes.
- Implement core components, recommendations, and principles from the prevailing Antimicrobial Stewardship Clinical Care Standard.
- Use the outcomes of audits on antimicrobial usage and appropriateness as a basis for ongoing quality improvement.
Action 3.19: Applying the antimicrobial stewardship program:
Organisations should ensure the program will:
- Periodically examine the patterns of antimicrobial prescribing and usage within the organisation.
- Leverage surveillance data concerning antimicrobial resistance to inform and improve appropriate prescribing practices.
- Assess the efficacy of the program, pinpoint areas needing enhancement, and initiate actions to better the appropriateness of antimicrobial prescribing and usage.
- Report to clinicians and governing bodies by:
- Delivering regular reports on compliance with the antimicrobial stewardship policy and guidelines.
- Highlighting areas requiring targeted interventions to combat antimicrobial resistance.
- Monitoring and reporting the organisation’s longitudinal performance related to the use and appropriateness of antimicrobials.
National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards
Requirement 3.3 (g): Minimising infection-related risks by implementing:
- Antibiotic prescribing and use practices for optimal care and antibiotic resistance reduction mechanisms
Action 5.2.1: Antimicrobial stewardship systems
Providers implements a system that:
- Complies with evidence-based, contemporary practice
- Is relevant to the service context.
Strengthened Quality Standards framework analysis - Aged Care Quality Standards
Failure to comply with the requirements could lead to an organisation being penalised or reprimanded.
Related Training Requirements Guides
The following Training Requirement guides can be used to support and facilitate the antimicrobial stewardship training requirement:
Skills Staff Need for Antimicrobial Stewardship
To excel in antimicrobial stewardship to enhance to provision of care, healthcare staff should possess specific skills:
| Skill | Key Elements |
|---|---|
| Effective Communication | Staff should be proficient in explaining treatment options to patients, including the risks and benefits of antibiotics. Effective communication ensures patients understand the importance of adherence to prescribed treatments, which can significantly impact the success of stewardship programs. |
| Diagnostic Proficiency | Staff should be adept at recognising clinical signs and symptoms of various infections. Rapid and accurate diagnosis allows for targeted treatment, reducing unnecessary antibiotic use. |
| Antibiotic Knowledge | Healthcare workers should be well-versed in different antibiotic classes, their mechanisms of action, and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains. This knowledge informs prescribing decisions and aids in preventing resistance. |
| Infection Prevention and Control | Staff should be trained in standard precautions, hand hygiene, and isolation protocols to prevent the spread of infections within healthcare settings. Effective infection control is a fundamental aspect of stewardship. |
| Data Analysis Skills | Healthcare professionals should be proficient in collecting and analyzing data related to antibiotic prescriptions and resistance patterns. Data-driven decisions are central to stewardship efforts. |
| Interdisciplinary Collaboration | Staff should be skilled in collaborating with pharmacists, microbiologists, and other specialists to determine the most appropriate antibiotic therapy, dosages, and durations. |
How to Assess Staff Competency in Antimicrobial Stewardship
Assessing staff competency in antimicrobial stewardship is critical to ensure that the training program is effective. Consider using various assessment methods:
- Written Exams: Administer written exams that cover antimicrobial stewardship principles, antibiotic classes, and resistance mechanisms. These exams evaluate the theoretical knowledge of the staff.
- Observation: Observe staff members in their interactions with patients. Assess their ability to communicate effectively, educate patients about antibiotics, and ensure adherence to prescribed treatments.
- Record Review: Review antibiotic prescription records to evaluate the appropriateness of antibiotic use. Look for instances of overuse or misuse, and assess whether the prescribed antibiotics align with established guidelines.
- Scenario-Based Assessments: Present staff with real-world scenarios involving antimicrobial decision-making. Evaluate their ability to make informed choices, considering patient history, lab results, and resistance patterns.
Strategies to Support Healthcare Staff Improve Antimicrobial Stewardship Skills
Supporting employees in developing skills for antimicrobial stewardship requires a multifaceted approach:
- Regular Training Sessions: Conduct regular training sessions on antimicrobial stewardship. These sessions should cover the latest guidelines, emerging resistance patterns, and case studies that highlight best practices.
- Educational Resources: Provide access to a repository of educational resources, including articles, videos, and guidelines. Encourage staff to stay updated on the latest developments in antimicrobial stewardship.
- Professional Development: Encourage staff to attend conferences, workshops, and seminars focused on antimicrobial stewardship. These events provide opportunities for networking and learning from experts in the field.
- Mentorship Programs: Establish mentorship programs where experienced healthcare professionals guide junior staff in antimicrobial decision-making. This hands-on approach fosters skill development and knowledge transfer.
- Feedback Mechanism: Implement a feedback mechanism where staff can receive constructive feedback on their stewardship efforts. Encourage open communication and continuous improvement.
- Simulation Training: Consider incorporating simulation-based training. Simulations allow staff to practice making antimicrobial decisions in a controlled environment, enhancing their decision-making skills.
Sample Training Plan for the Antimicrobial Stewardship Training Requirement
Antimicrobial stewardship skills can be reinforced and strengthened with an effective training plan based on your organisation's specific requirements.
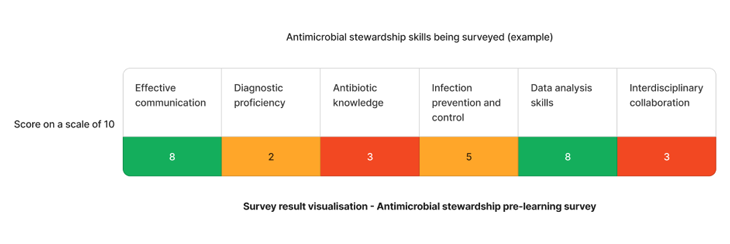
Using the above needs assessment survey as an example - The skills that requires the most attention are antibiotic knowledge and interdisciplinary collaboration skills. We can target learning initiatives to fill these gaps to enhance staff competency.
| Quarter | Topics | Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Antibiotic knowledge | |
| Q2 | Interdisciplinary collaboration |
Need an LMS that can support antimicrobial stewardship learning?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support with your antimicrobial stewardship requirements!
Staff Competency Assessment for Antimicrobial Stewardship - Example
The following is an example survey that learning and development coordinators may use to asses staff competency in antimicrobial stewardship.
Staff Survey - Antimicrobial Stewardship Competency
-
What are the key principles of antimicrobial stewardship?
- [Answer here]
-
How do you communicate with patients about antibiotic usage?
- [Answer here]
-
Can you identify signs of antibiotic resistance?
- 1. Yes
- 2. Somewhat
- 3. No
-
What infection control measures are essential in antimicrobial stewardship?
- [Answer here]
-
Describe a scenario where interdisciplinary collaboration was crucial in antimicrobial decision-making.
- [Answer here]
-
How do you analyze data related to antimicrobial usage?
- [Answer here]
Conclusion
By adhering to the outlined standards and focusing on the specific skills needed, you can ensure that your staff is well-prepared to make responsible antimicrobial decisions, ultimately benefiting patient care and public health.
Remember that the landscape of antimicrobial stewardship is constantly evolving. Regularly update your training program to reflect the latest guidelines and best practices.
References
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'NSQHS Preventing and Controlling Infections Standard'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 3.18'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. 'NSQHS Action 3.19'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Aged Care Quality Standard - Personal and clinical care - 3.3 (g)'
- Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission, 2023. 'Stronger Standards, Better Aged Care Program - 5.2.1'
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health, 2023. Antimicrobial Stewardship Clinical Care Standard


